A Gas Power Generator is an essential tool for any home or business that wants to ensure a reliable source of backup power. For those who live in areas prone to power outages, a gas power generator can be a lifesaver. Gas power generators offer a cost-effective and reliable source of electricity that can be used in the event of a power outage or other emergency. With a gas power generator, you can be sure that your home or business will have the power it needs when it matters most.
Types of Gas Powered Generators
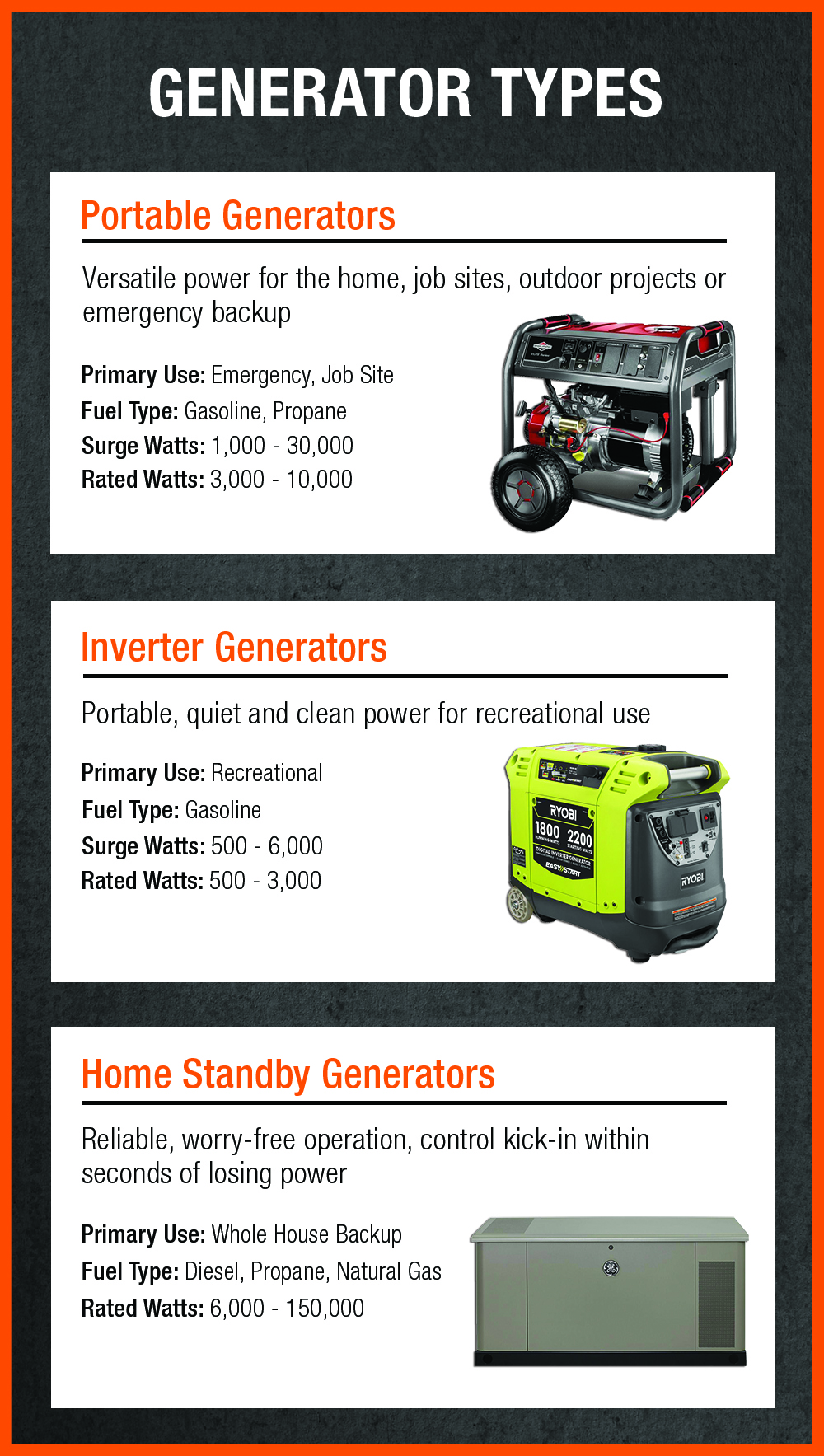
1 Portable Generators
Portable generators are the most common type and are typically used by homeowners for short-term power outages. They are usually powered by gasoline and are easy to move around, making them an ideal choice for camping trips, tailgating, and other activities.
2 Standby Generators
Standby generators are a more powerful and expensive option, designed for long-term power outages. They are typically powered by natural gas or propane and are permanently mounted outside of the home. They are usually connected to the home’s electrical system, so they can automatically provide power during a power outage.
3 Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are the most efficient type of gas-powered generator, as they produce a cleaner, more consistent power than other types. They are typically smaller, quieter, and more portable than other types, making them ideal for camping and recreational use.
Benefits of Gas Powered Generators

- Increased fuel efficiency – Gas powered generators have significantly better fuel efficiency compared to other types of generators, making them more cost-effective to operate.
- Quiet Operation – Gas powered generators are generally much quieter than other types of generators, making them ideal for use in residential and commercial settings.
- Versatility – Gas powered generators can be used to power a wide range of appliances, from lights and air conditioners to large industrial machines.
- Low Maintenance – Gas powered generators require much less maintenance than other types of generators and can often last for years with only minimal upkeep.
- Portability – Gas powered generators are typically much lighter and more portable than other types of generators, making them ideal for those who need to move their generator from one location to another.
Advantages of Inverter Generators
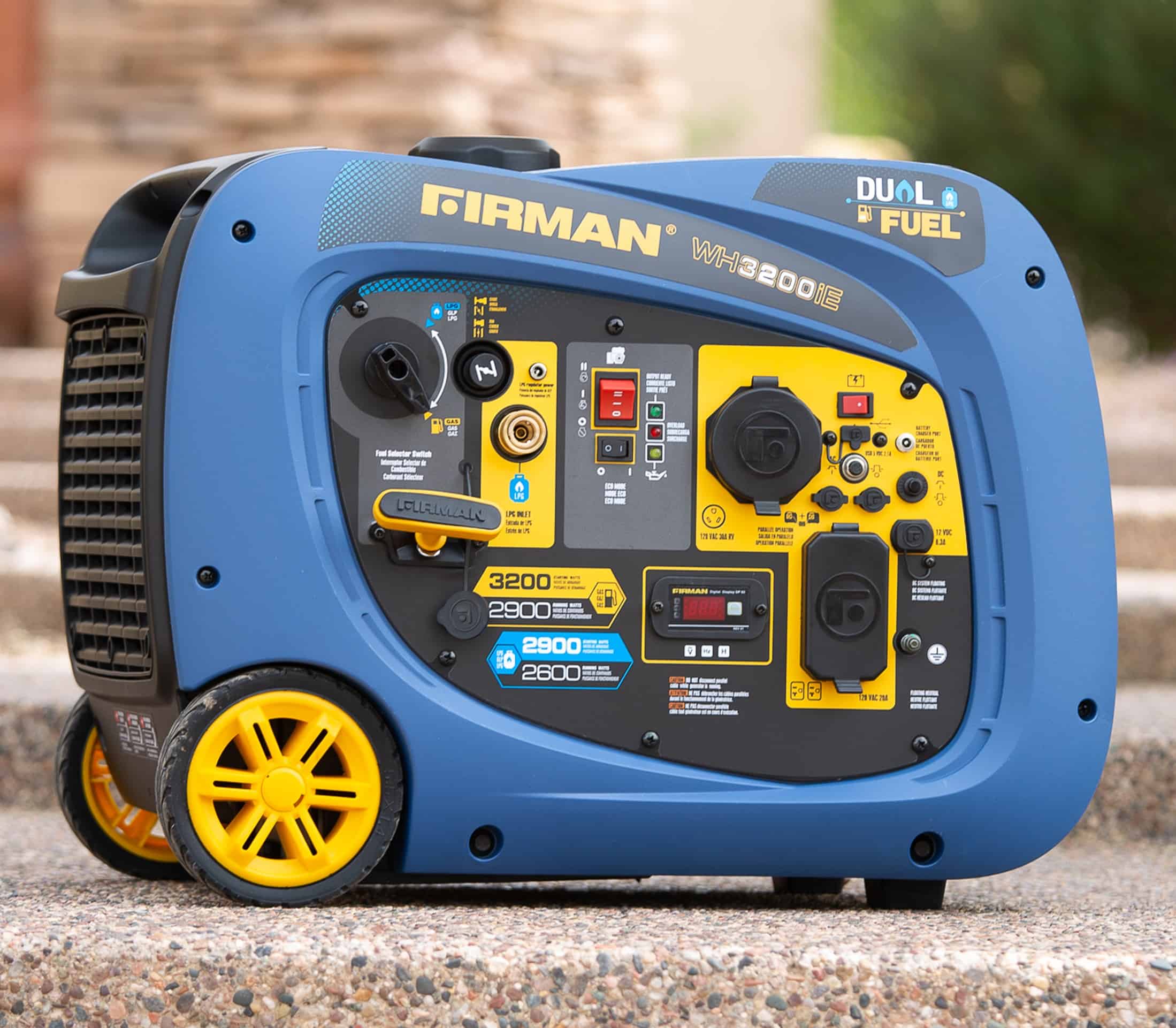

Inverter generators are a popular choice among gas power generator users, as they offer numerous advantages. The main benefit of inverter generators is that they provide clean and stable power, meaning that devices with sensitive circuitry can be powered safely. They are also smaller, lighter and quieter than traditional generators, making them more portable and less disruptive to their surroundings. Inverter generators typically use less fuel than traditional generators, making them more fuel-efficient and cost-effective over time. Additionally, they are designed with advanced safety features to protect against overloads and surges.
Disadvantages of Gas Powered Generators

- Noise Pollution: Gas powered generators are typically loud, making them unsuitable for use in residential areas.
- Vulnerability to Theft: Gas powered generators can be more easily accessed by thieves than other types of generators.
- Emissions: Gas powered generators produce more emissions than other types of generators, making them less environmentally friendly.
- Cost: Gas powered generators are typically more expensive than other types of generators.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is required to keep gas powered generators running at peak performance.
- Fuel Storage: Gasoline and other fuels used in gas powered generators need to be stored safely and properly.
Maintenance of Gas Powered Generators

Gas powered generators require regular maintenance to ensure they run smoothly and safely. The most important maintenance tasks include regular inspection, cleaning, and oil and filter changes.
Inspection should be done at least every three months, or more frequently in areas where there is a lot of dust or debris. During the inspection, check for any signs of damage or wear, such as frayed wires, loose connections, or worn out parts.
Cleaning is also important to ensure the generator runs efficiently. Clean off any dirt or debris on the exterior. Use a vacuum to clean the interior of the generator, including the air filter, spark plug, and fan.
Oil and filter changes should be done every 3 months or 500 hours of operation. Change the oil and oil filter, as well as the air filter. Make sure to use the correct type of oil for your generator.
Following these maintenance tasks will help keep your generator in good condition and running safely. It is also important to inspect the generator before each use and to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for use and maintenance.
Safety Considerations
| Safety Issue | Suggested Solution |
|---|---|
| Carbon Monoxide Poisoning | Install carbon monoxide detectors close to the generator and ensure proper ventilation to the outside. |
| Electric Shock | Do not use the generator in wet conditions and use GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets where possible. |
| Fire Hazard | Ensure proper clearance from combustible materials and keep the generator clean and well-maintained. |
| Noise Pollution | Position the generator away from noise-sensitive areas and use soundproofing material to minimize the sound. |
| Fuel Storage | Store fuel in an approved container, away from the generator, in a cool and well-ventilated area. |
Fuel Types Suitable for Gas Powered Generators
| Fuel Type | Common Uses |
|---|---|
| Gasoline | Residential, commercial and industrial uses |
| Propane | Residential, commercial and industrial uses |
| Natural Gas | Industrial and commercial uses |
| Diesel | Commercial and industrial uses |
Gas powered generators are typically powered by one of four fuel types: gasoline, propane, natural gas and diesel. Gasoline is the most commonly used fuel for residential, commercial and industrial applications, while propane is also used for residential, commercial and industrial purposes. Natural gas is most commonly used for industrial and commercial applications, while diesel is used primarily for commercial and industrial applications.
Cost Considerations
Gas power generators are typically more expensive than other types of power generators. The initial cost of purchase includes the price of the generator, fuel tank, and any necessary installation and setup. Additionally, gas power generators require more frequent maintenance, such as changing the oil, spark plugs, and air filters, as well as refueling, which can add up to significant ongoing costs. It is important to factor in all of these costs when deciding on the best type of generator for a particular need.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Gas Powered Electric Generator?
A gas powered electric generator is a device that uses natural gas to produce electricity. It works by converting the chemical energy of the natural gas into mechanical energy, which is then converted into electrical energy. The generator typically consists of an engine, alternator, fuel tank, and exhaust system. The engine burns the natural gas to produce a mechanical force that spins the alternator, which produces electricity. The generator is then connected to a power grid or electrical circuit to provide power to homes and businesses.
What are the benefits of a gas operated generator?
A gas operated generator has the advantage of being highly portable and economical. It is also relatively easy to maintain and operate. Gas powered generators are highly durable and can run for long periods of time without requiring refueling. Additionally, gas powered generators are generally quieter than diesel powered generators and produce fewer emissions. Finally, gas powered generators are often less expensive than other types of generators.
What is the Difference Between a Gasoline Electric Generator and a Gas Powered Generator?
A gasoline electric generator is powered by an internal combustion engine that runs on gasoline, while a gas powered generator is powered by a gas turbine engine that runs on combustible fuels such as natural gas, propane, or diesel. Gasoline electric generators are typically less expensive than gas powered generators, but they are also less efficient, have a shorter lifespan, emit more pollutants, and require more frequent maintenance. Gas powered generators are more efficient, have a longer lifespan, and require less maintenance than gasoline electric generators, but they cost more and emit fewer pollutants.
What are the advantages of having a gas powered generator as a backup source of power?
Gas powered generators are a reliable and convenient way to provide backup power during an outage or emergency. They are relatively affordable, easy to install, and can be easily maintained. They are also highly efficient and can generate more power than other types of generators. Additionally, gas powered generators are portable and can be transported to wherever power is needed. Finally, gas powered generators are a clean energy source, as they produce fewer emissions than other types of fuel sources.
What makes a gas power generator the ultimate backup source of power for my home or business?
Gas power generators are the ideal backup source of power for homes and businesses because of their reliability, affordability, and portability. They provide a dependable source of power in the event of a power outage, and are usually able to power multiple devices and appliances. Gas power generators are also cost-effective and can be easily stored in a garage or outbuilding. They are also relatively easy to operate, making them the perfect solution for homes and businesses that require backup power.
Conclusion
A gas power generator can be a great solution for those looking for an efficient and reliable backup source of power for their home or business. It is a cost-effective and powerful option for emergency power needs, and can provide reliable power for a variety of applications. Additionally, gas power generators are easy to use and maintain, making them a great option for those who want to be prepared for potential power outages.







