Are you looking for a way to generate electricity in order to meet your electricity needs? A generator for electricity is an ideal solution for those who are looking for a reliable power source. Generators can be used to provide electricity for a variety of applications, from powering homes, businesses, and recreational vehicles to providing emergency power during times of power outages. This article will explore the different types of generators available and how each one works to generate electricity. Additionally, we will discuss the benefits of using a generator for electricity, as well as tips for selecting the right generator for your needs.
Types of Generators

| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Gasoline Generator | Runs on gasoline to produce electricity. Commonly used for emergency situations. |
| Diesel Generator | Runs on diesel fuel to produce electricity. Commonly used for industrial applications. |
| Natural Gas Generator | Runs on natural gas to produce electricity. Commonly used for powering homes and businesses. |
| Wind Turbine Generator | Runs on wind energy to produce electricity. Commonly used for renewable energy applications. |
| Solar Panel Generator | Runs on solar energy to produce electricity. Commonly used for renewable energy applications. |
Fuel Generator


Fuel generators are an efficient and reliable way to generate electricity. They convert fuel such as diesel, petrol, natural gas, propane, or biogas into electrical energy which can be used for residential, commercial, industrial and agricultural purposes. Fuel generators are powered by internal combustion engines which are used to turn electric generators and produce electricity. They are easy to install and maintain and can provide a reliable source of electricity during power outages. Fuel generators come in a variety of sizes and power capabilities and are available for both stationary and portable applications.
Solar Generator


| Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
| Renewable energy source | Expensive to install |
| Low maintenance | Weather dependent |
| No pollutants | Efficiency decreases over time |
Solar generators use solar energy to generate electricity. Solar panels are used to collect energy from the sun, which is then converted into electricity by an inverter. Solar generators are popular due to their renewable energy source, low maintenance, and lack of pollutants. However, they are expensive to install and their efficiency decreases over time. Additionally, solar generators are weather dependent and may not be able to produce electricity if the weather is not favorable.
Wind Generator
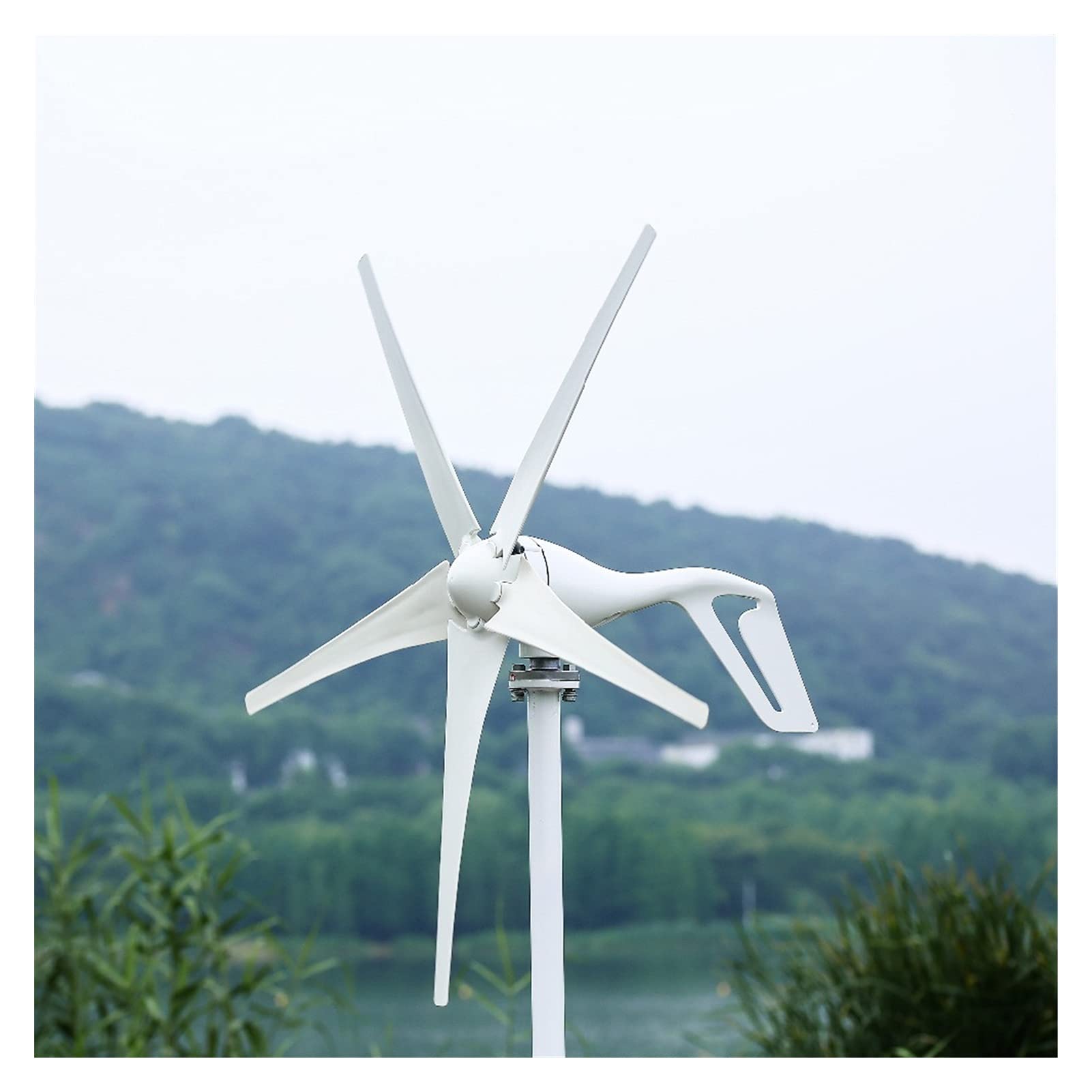


Wind generators are machines that use the kinetic energy of the wind to generate electricity. The main components of a wind generator are the rotor, the blades, the gearbox, the generator and the tower. The rotor consists of the blades that capture the wind and convert its kinetic energy into mechanical energy. The blades are connected to a gearbox which increases the speed of the rotor and transfers the mechanical energy to the generator. The generator then converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. Wind generators are usually installed on tall towers to increase their efficiency, as the wind speed increases with altitude. Wind generators are becoming increasingly popular as a source of renewable energy, as they are clean, efficient and cost-effective.
Hydro Generator


- A hydro generator is a type of electrical generator that uses the energy of falling or fast-flowing water to produce electricity.
- It is a type of turbine generator, which converts kinetic energy into electricity.
- The most common type of hydro generator is a water wheel, which is a large wheel that is turned by the force of water flowing over it.
- Other types of hydro generators include Francis turbines, Pelton turbines, and Kaplan turbines.
- The hydro generator works by allowing the water to flow through the turbine, which causes the turbine to rotate, creating a magnetic field that generates electricity.
- The electricity produced by the hydro generator can then be used to power homes, businesses, and other electrical appliances.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Generators
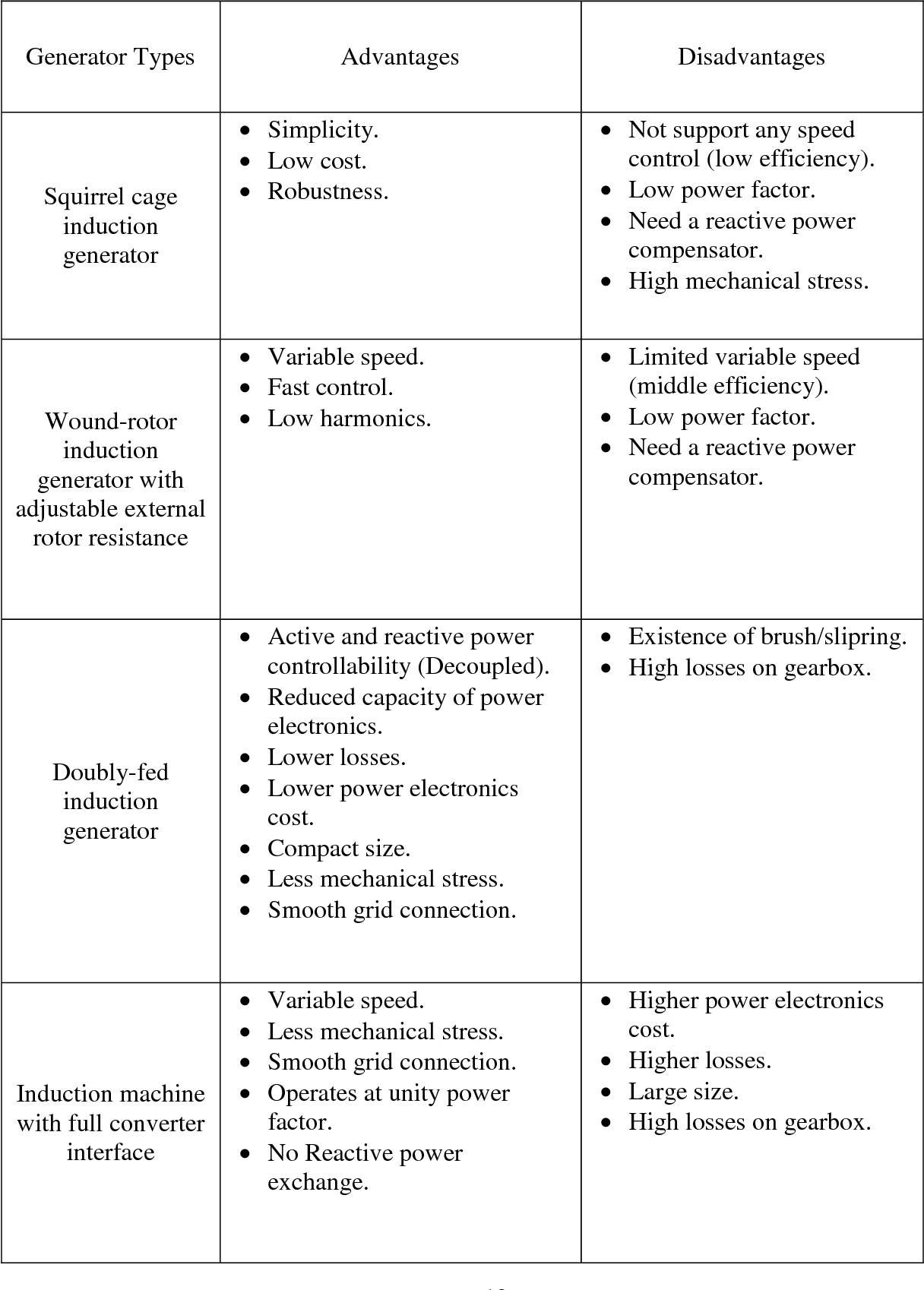
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Fuel Generator


A fuel generator is a generator powered by a fuel source such as diesel, gasoline, or propane. The fuel is used to power an engine, which in turn produces electrical energy. Fuel generators provide a reliable source of electricity, especially in remote areas where other sources of power are not available.
Fuel generators are typically used for powering large industrial and commercial applications. They can be used to power homes, businesses, factories, construction sites, and other large power needs. Fuel generators are typically very efficient and can produce large amounts of power, depending on the size and type of fuel used.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Reliable source of power | Cost of fuel |
| Produce high amounts of power | Noise pollution |
| Efficient | Maintenance required |
| Portable | Emissions |
Fuel generators are often used as a backup power source or in places where access to other sources of electricity is not available. They are also used in emergency situations, when power outages occur. Despite their advantages, fuel generators can be expensive to operate and maintain. They also produce noise and emissions, which may be a concern for some users.
Solar Generator


Solar generators are an increasingly popular choice for electricity generation. They use sunlight to generate energy, and are more efficient and cost effective than other renewable energy sources. Solar generators are easy to install and maintain, and produce no emissions. They are also extremely reliable and can be used to power a variety of appliances and devices. Solar generators are often used in remote or off-grid locations, as they are a great alternative to burning fossil fuels or relying on a traditional power grid. Solar generators come in a range of sizes, from small portable units to large stationary systems. They can also be used to supplement existing energy sources, helping to reduce energy costs. Solar generators are a great way to reduce your carbon footprint and support a more sustainable lifestyle.
Wind Generator


| How it works | A wind turbine converts the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then converted into electricity by means of an electric generator. |
| Advantages | Renewable energy source, Low operating cost, Low maintenance cost, Low noise emission, No pollutants |
| Disadvantages | High initial investment, Intermittent source of energy, Limited applications, Unpredictable energy output |
Hydro Generator


A hydro generator is a device that uses the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. It does this by converting the energy of the flowing water into mechanical energy, which is then converted into electrical energy. The generator is typically situated in a river or lake and is connected to a dam, which controls the flow of water. The generator’s blades are turned by the flow of water, which turns a turbine and produces electricity. Hydro generators are one of the most efficient and reliable sources of electricity, and are often used to supplement other sources of electricity, such as wind and solar. They can also be used to generate large amounts of electricity, making them a cost-effective and reliable source of energy.
What is a Generator for Electricity?
A generator is a machine that produces electricity from mechanical energy. It generally works by using an engine to spin a rotor, or wheel, which produces electricity through electromagnetic induction. Generators can be used to produce electricity for homes, businesses, and other applications. Depending on the type of generator, they can produce either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) electricity. Generators can be powered by a variety of sources, including gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or renewable sources such as solar, wind, and water. Generators are also used to provide backup power in case of a power outage.
Common Uses of Generators
- Backup Power Supply: Generators are often used as backup power supply in case the main power supply fails due to a power outage.
- Emergency Power Supply: Generators are used in emergencies to supply power for essential equipment and systems.
- Portable Power Supply: Generators are used for providing power for outdoor activities such as camping and tailgating.
- Industrial Power Supply: Generators are used in industrial and commercial settings for powering large equipment and machinery.
- Power for Construction Sites: Generators are used in construction sites for providing power for tools and equipment.
How to Choose a Generator
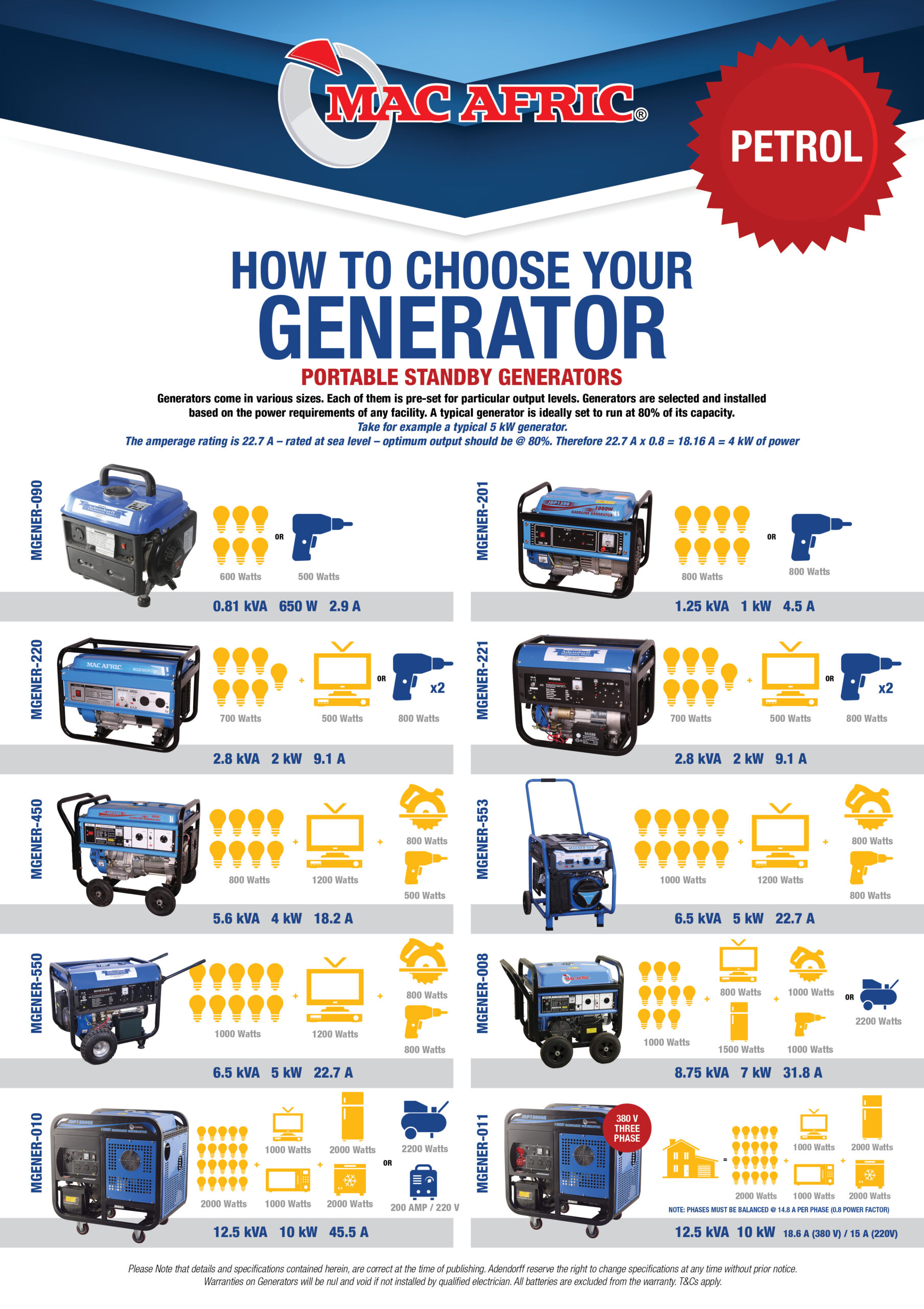
It is important to choose a generator that is powerful enough to handle your electricity needs. Consider the wattage of the generator, as well as the type of fuel it uses. Make sure the generator is large enough to support the appliances and electronics you need to power.
You should also consider the size of the generator and how much noise it will produce. Larger generators can produce more power, but they can also be louder and more expensive. Portable generators can be easier to move, but they may not be able to provide enough power for larger appliances.
Safety is another important factor when choosing a generator. Make sure the generator meets safety standards and is equipped with an automatic shut-off system. Consider the type of fuel the generator requires, as well as any accessories you may need to safely operate the generator.
Finally, consider the cost of the generator. Generators come in a range of prices, so choose one that fits within your budget. Make sure you factor in the cost of fuel, as well as any maintenance expenses. With the right generator, you can ensure you have a reliable source of electricity.
Safety Considerations When Using a Generator
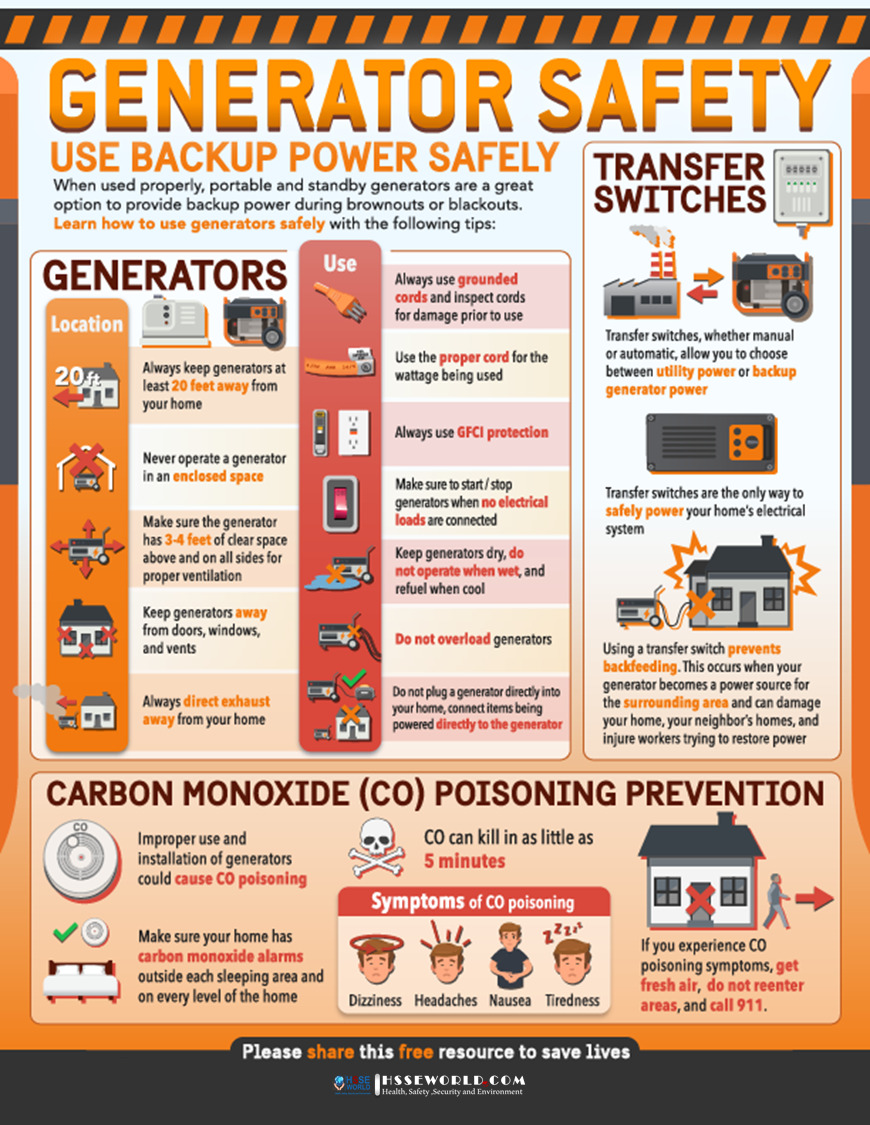
- Never use a generator indoors, as they emit carbon monoxide which is deadly.
- Always read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions before operating a generator.
- Ensure the generator is properly grounded.
- Keep the generator away from combustible materials.
- Use an extension cord when needed to connect the generator to the appliance.
- Do not overload the generator, as it can be damaged.
- Allow the generator to cool before refueling.
- Never touch a running generator with wet hands.
Maintenance of Generators
- Always check the engine oil level.
- Check the air filter and replace it if necessary.
- Check the fuel filter, fuel lines and fuel pump.
- Check the spark plug and replace it if necessary.
- Perform periodic engine tune-ups.
- Check the coolant level and condition.
- Check the battery and charging system.
- Check the exhaust system for any blockages.
- Check the generator’s voltage regulator.
- Check the generator’s voltage output.
- Check the generator’s control panel.
- Test the generator regularly.
- Perform routine maintenance, such as cleaning or lubricating the generator.
Cost of Generators
- Small portable generators – $300-$1000
- Standby generators – $3000-$10000
- Commercial/industrial generators – $5000-$50000
The overall cost of a generator depends on the size and power output required. Smaller portable generators are the most cost-effective and can provide enough power for basic needs such as powering lights and small appliances. Standby generators are larger and more powerful and can be used to power larger appliances and even a whole house. Commercial and industrial generators are the most expensive as they offer the highest power output and are used for heavy-duty applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Electrical Current Generator?
An electrical current generator is a device that produces an electric current by mechanically turning a generator shaft. This device can be used to produce electricity for a variety of purposes, such as powering lights, appliances, and other electrical equipment. Generators vary in size and power output, and can be powered by a variety of sources, including gasoline, diesel, natural gas, nuclear, and solar energy. Generators can also be used to provide back-up power in the event of an electrical outage.
How does a generator for electricity help meet my electricity needs?
A generator for electricity is a great way to provide a reliable and constant source of electricity in times of need. Generators can be used to provide emergency power when the grid is down, or to provide supplemental power when the grid is overloaded. Generators can also be used to supplement renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, when their output is insufficient. Generators come in a variety of sizes and types, from small portable units to large commercial-grade models. No matter what your electricity needs are, a generator can provide a reliable source of power that will help you meet those needs.
What are the advantages of using a generator for electricity?
Generators offer a reliable and consistent source of electricity. They are easy to operate and provide a cost-effective way to power homes, businesses and other facilities. Generators can provide power in areas where the electrical grid has been damaged or disrupted, or when backup power is needed. Unlike traditional sources of electricity, generators can be used to produce electricity on demand. Generators are also highly portable and can be used in areas where access to the electrical grid is limited.
How does a Generator for Electricity Work?
A generator for electricity works by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. This is done through the use of an alternator. The alternator is driven by an engine, typically a gasoline engine. The engine turns the alternator which contains a coil of copper wire. As the coil spins, it passes through a magnetic field, causing a current to be generated in the wire. This current is then sent to a transformer, which increases the voltage, allowing it to be used for electricity.
What are some common uses for a generator for electricity?
A generator for electricity is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Generators are commonly used as backup power sources for homes and businesses when the power grid fails. They are also used for emergency power for medical facilities, for powering tools on construction sites, for recreational activities such as camping, and for providing supplementary power to remote locations. Generators can also be used to provide power for events such as concerts or sporting events.
Conclusion
Generators provide a convenient and cost-effective way to meet your electricity needs. Generators are available in a variety of sizes and fuel types, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. They can be used to back up your electrical system in the event of a power outage, or for emergency power during natural disasters. Generators are also a great choice for powering remote or off-grid locations. With the right generator, you can rest assured that your electricity needs will be met.







